Land Transport Innovation Portal
What is the Land Transport Innovation Portal?

The Land Transport Innovation Portal supports the development of innovative solutions to meet the Land Transport Master Plan 2040 (LTMP 2040) goals.
Through this portal, you can:





Submit your Ideas
Have an idea to help us reach our land transport goals? Submit an abstract of your proposed solution through our Submission Form. If your proposed idea matches what we are looking for, we will get in touch with you to find out more!
Who can apply?
Local and global organisations (e.g. private companies, research institutes or institutes of higher learning). Organisations should set up a base in Singapore to run the project and also own, manage and exploit rights of all intellectual property that is developed.
Proposed solutions will be evaluated broadly based on, but not limited to the following criteria:
| Criteria | Description |
|---|---|
| Objective |
|
| Innovativeness |
|
| Scalability & Implementation |
|
Shortlisted solutions will be funded based on the duration, scalability and readiness of technology. Funding requirements and details will be determined based on the project.
Contact Us
Reach out to us through our Contact Form for more assistance.
Join Our Mailing List!
Join our Mailing List to receive updates on the latest land transport innovation news!
UMI Grant Call – Road Safety and Traffic Management through Expanded Data Analytics and Advanced Research
As Singapore experiences continued development through increasing economic activities and maturing townships, traffic interactions between road users have become increasingly complex within our densely populated environment. These interactions involve public and private buses, cars, taxis, motorcycles, active mobility users and pedestrians. At the same time, the advancement of geographical information technology and AI has allowed for better sensemaking capabilities across the public and private sector.
Through the integration of safety research and advanced technologies such as machine learning, computer vision, sophisticated data collection and analysis, and recommendation engines, AI-assisted tools can bring together multiple datasets, analyse traffic flow patterns and road user behaviours, map complex relationships between road users and infrastructure, among many others. This helps to support the implementation of targeted safety measures early, thereby reducing the occurrences of traffic accidents, especially of severe injuries, and improve overall safety and efficiency of the road network.
Objective
This grant call seeks to initiate a deep-dive research, through development of a data-driven and AI-assisted analysis solution framework, to generate comprehensive road safety insights to strengthen LTA's capabilities to design safer road layouts, implement upstream safety measures and develop evidence-based policies.
Application Process and Submission
This call is open to all R&D organisations in Singapore including publicly-funded IHLs, not-for-profit research institutions, public sector agencies, private companies, and company-affiliated research entities.
The lead Principal Investigator (PI) and Co-Lead Principal Investigator (Co-PI) are responsible for delivering the outcomes of the project and will be required to have a minimum of 9 months of residency per year in Singapore. All work should be done in Singapore, unless expressly approved by LTA.
All applications and supporting documents for the grant call must be submitted by 21 Oct 2025, 5pm (SGT/GMT+8) to LTA_Innovate@lta.gov.sg. Only documents in Word, Excel and PDF formats will be accepted.
For applicants from IHLs and A*STAR Research Institutes, please submit your proposals through your respective research offices and obtain your Director of Research’s endorsements.
LTA will conduct a briefing to provide clarifications on the grant call on 17 Sep 2025 at the Land Transport Authority (LTA), if a sufficient number of registrations is received. If you are interested to attend the briefing, please register by 12 Sep 2025, 5pm. All registered attendees will receive a confirmation via email on or after 15 Sep 2025.
Documents for submission
- Annex C Budget Template (xlsx, 41kB)
- Annex D Project Milestones and Deliverables (docx, 30kB)
- Annex E Offline Application Package (xlsx, 31kB)
Documents for information
- (Revised 18 Sep 2025) Grant Call Factsheet – Road Safety and Traffic Management through Expanded Data Analytics and Advanced Research (PDF, 195kB)
- Full Proposal Guidelines (PDF, 215kB)
- List of Non-Fundable Direct Costs (PDF, 102kB)
- Guidelines for the Management of Research Grants (PDF, 99kB)
- Research Grant Terms & Conditions (as of 1 Jan 2020) (PDF, 146kB)
[Update 18 September 2025]: There are some updates to the Grant Call Factsheet, which will supersede the previous version. Please ensure you refer to this latest information instead.
For more information such as the proposal guidelines and evaluation criteria, please refer to the Grant Call Factsheet. For enquiries on this grant call, please email LTA_Innovate@lta.gov.sg.
Call for Solutions – Condition Monitoring and Detection System for Bukit Panjang LRT
The Bukit Panjang Light Rapid Transit (BPLRT) system operates with a fleet of 32 vehicles, with maintenance activities conducted during engineering hours between daily operations. A critical aspect of the maintenance regime involves inspecting the power rails, which are specialised tracks that deliver electrical power to the trains. These inspections are crucial for identifying and timely addressing maintenance issues that could potentially trigger abnormal flashover events at the power rails. In more serious events, flashovers could lead to potential disruption of BPLRT service. Currently, such inspections are carried out manually during engineering hours.
To enhance the existing maintenance regime, LTA is seeking to implement a condition monitoring and/or detection system which aims to provide a more efficient and accurate means to identify power rail misalignments and surface defects. The system would allow LTA and the Public Transport Operator (PTO) to be more effective and productive in addressing such defects early by having an accurate and timely defect detection system to support targeted maintenance interventions. This will ultimately improve the overall reliability of the BPLRT system to serve our commuters better.
The project will proceed in 2 phases. Phase I will be the Proof-of-Concept of a limited trial of the solution on a single BPLRT vehicle. After successfully completing Phase I with satisfactory results, the solution will be trialled under operational settings with real-time monitoring and reporting function in Phase II.
Please refer to the Problem Statement Brief – Condition Monitoring and Detection System for Bukit Panjang LRT (PDF, 323kB) for more details.
[Update on 31 July 2025]: There are some updates to the information below, which will supersede the details found in the Problem Statement Brief. Please ensure you refer to this latest information instead.
LTA will hold a briefing and a site visit to provide more information on the problem statement on 8 August 2025 at the Land Transport Authority (LTA) – Hampshire Office (Hampshire Road, Singapore 219428). If you are interested to attend the briefing to better understand the design interface between the current collector assembly to power rail, please register by 1 August 2025, 4pm (SGT/GMT+8). Please be advised that participants are expected to submit a softcopy of the signed Non-Disclosure Agreement for CFS Condition Monitoring and Detection System for Bukit Panjang LRT (PDF, 180kB) before they can attend the briefing. Details on the site visit will be shared during the briefing.
All proposals must be submitted by 30 September 2025, 4pm (SGT/GMT+8) via this submission form. LTA will contact the shortlisted solution providers separately after the CFS closes.
Please submit any queries regarding this Call for Solutions via this form no later than 9 September 2025, 4pm (SGT/GMT +8). LTA’s responses to the queries will be updated on Land Transport Innovation Portal before the close of the Call for Solutions.
[Update on 18 September 2025]: Please find the consolidated responses (PDF, 204kB) to the submitted queries for this Call for Solutions.
Land Transport Sandboxes
LTA facilitates the development and use of new technologies which are not within the scope of current standards and regulations through a sandbox arrangement. This allows a safe environment to better understand the use, benefits, and associated risks of the new technologies within our local context. Interested applicants can check out the available thematic sandboxes to submit your innovation proposals.
Sandbox for Electric Vehicle Charging Systems (EVCS)
Currently, all Electric Vehicle Charging Systems (EVCS) used in Singapore must comply with existing standards and regulations, such as the Technical Reference 25 (TR25). Advancements in Electric Vehicles (EV) charging technology have led to an increased number of EVCS deploying new technologies which are not covered under the scope of current standards, even as we regularly update these standards.
A responsive and forward-looking regulatory approach will help facilitate the deployment and development of such innovative EVCS. To achieve this, LTA has established an EVCS sandbox framework where such systems can be trialled in a controlled environment.
Closed Applications to Sandbox
- Electric Heavy Goods Vehicle (e-HGV) Battery Charging and Swapping System (BCSS) Solutions. Awarded to PSA Corporation Ltd and a consortium comprising Strides Frontier Pte Ltd and Ecoswift Pte Ltd to trial and assess the viability of battery swapping for e-HGVs.
- Electric Vehicle Mobile Charging System (MCS) Solutions. Awarded to Power-Up Tech Pte Ltd and Beecharge Innovation Group Pte Ltd, to trial and assess the viability of mobile EV charging forelectric vehicles.
General Sandbox Enquiry Form
For general enquiries about LTA’s sandboxes, please use our online form.
Data to Support Innovation Work
Enterprises, third-party developers, researchers, and the general public can obtain information from the Land Transport DataMall. This includes:
Open Datasets
- Static Datasets comprise mostly the Geographical Information System (GIS) information available in the ESRI shape file format. LTA’s statistical monthly/annual reports available in PDF and XLS formats.
- Dynamic Datasets are updated live. They are served out via APIs which are accessible with an Account Key. This is issued only to registered DataMall subscribers.
On-Request Datasets
LTA can share other datasets on a case-by case basis. This is to address requesters’ needs, while meeting LTA’s commitment to data confidentiality and privacy.
The datasets available are listed in DataMall’s “On-Request Datasets” tab. More specific information can be found within metadata in each dataset.
Two new on-request datasets are uploaded on the DataMall:
- Taxi Movement Data
- Traffic Lights Traffic Plans
To request data, requestors should download and complete the Data Sharing Form and submit it via the Contact Us page on DataMall.
Innovation @ LTA

We are able to bring innovative ideas to life thanks to collaborations with industry and research partners! We aim to deliver a safe, reliable, inclusive, cost efficient and environmentally-sustainable land transport system for our commuters.
Read more about our latest innovation projects here!
Encouraging Car-Lite and Promoting Walk-Cycle-Ride (WCR) Transport Modes Through a Digital Journey Planner Prototype
- Industry Partner: Nippon Koei Business Partners Co., Ltd.
- LTA User: Transport Planning Data & Technology Division (P&P)
LTA explored solutions to encourage drivers to embrace more car-lite modes, through the Jurong Lake District (JLD) Innovation Challenge hosted on IMDA’s Open Innovation Platform.
Leveraging Behaviour Nudge Theory to Influence Transport Choices
Together with Nippon Koei (NK), an innovative “journey planner” prototype was developed to encourage sustainable transport adoption, by providing real-time behavioural nudges to drivers to encourage switching from private car usage to Walk-Cycle-Ride (WCR).
This is enabled through the 3 key features developed and tested:
1. Real-time Mobility Classification and Location Inference
Through a software development kit (SDK), the “journey planner” was able to integrate seamlessly with third-party applications. This enables the collection of mobility and lifestyle data of users through:
- Real-time classification of Walk-Cycle-Ride transport modes using mobile sensors including gyroscope, accelerometer, Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS);
- Inference of significant locations such as home and work; and
- Detection of user lifestyle preferences based on frequently visited points of interest (POIs).
The collection of these data allows the “journey planner” to understand users’ travel patterns and lifestyle behaviours, providing appropriate nudges to influence their travel choices.
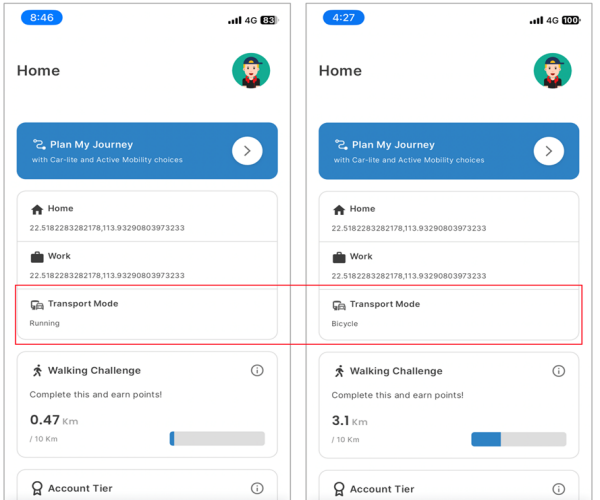
Backend feature in the SDK classifying the transport mode using mobile sensors in real-time
2. AI-Driven Persona Generation
The persona engine harnesses machine learning algorithms and generative AI to analyse anonymised mobility data patterns gathered via SDK. Through this analysis, the engine segments users into four distinct behavioural profiles:
- Cost-conscious
- Eco-conscious
- Time-conscious
- Health-conscious
Based on these behavioural personas, nudges are delivered as interactive cards that align with each user’s primary motivations. These challenge cards are displayed prominently above other features, ensuring users encounter activities that resonate with their wellness priorities first.
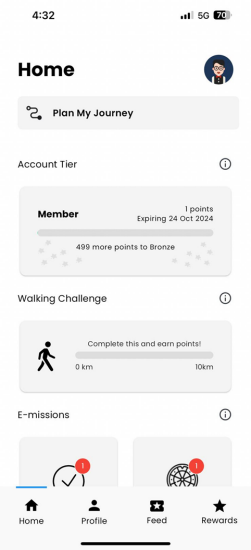
A “Walking Challenge” card prioritised for a user identified as “health-conscious” to encourage walking
3. Data Analytics for Transport Planning
A user-friendly web dashboard that offers visibility into mobility trends through its analytics capabilities such as:
- Aggregated data on weekday versus weekend car usage, trip types, and transport modes
- User profiles, such as home or work location heatmaps and inferred lifestyle preferences
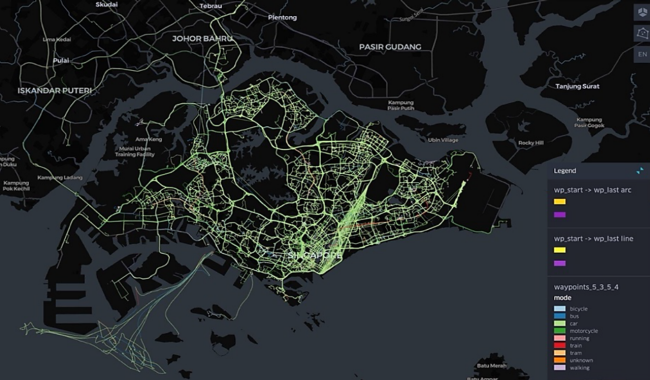
Dashboard visualising mobility patterns and trends
Nudging Sustainability Forward
The prototype successfully demonstrated the feasibility of using digital features for persona segmentation and behavioural nudging, showing its potential in supporting Singapore’s transition towards sustainable transportation. Its SDK allows for the prototype to integrate into most third-party applications used by drivers, making it versatile enough to support diverse use cases across different platforms.
Other innovation projects you may find interesting:
- Enhancement of Roadworks Application Process using Artificial Intelligence (PDF, 77kB)
- Viaduct Bearing Inspection with Drones (PDF, 111kB)
- Redesigning Temporary Bus Shelters (PDF, 252kB)
- Enhancing Utilities Visualisation in Construction Works with Augmented Reality (AR) (PDF, 343kB)
- AI-Powered Road Maintenance with Mobile Geotagging (PDF, 147kB)
- Paving the Way for Eco-Friendly Roads